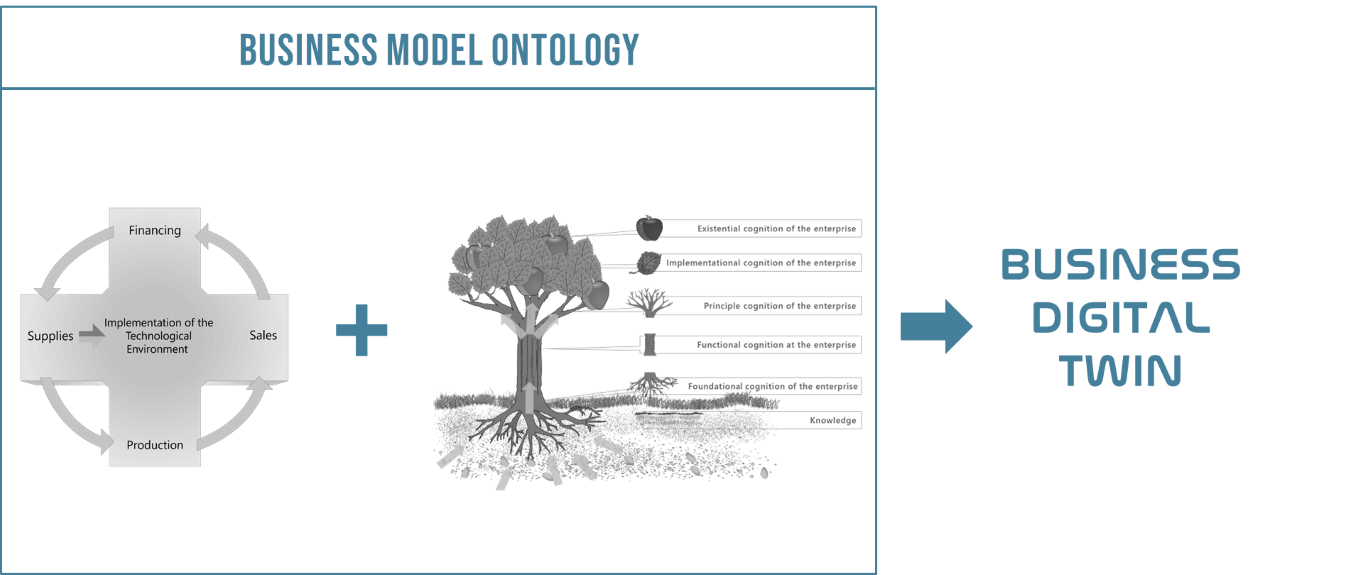
Business Digital Twin
The Business Digital Twin is a cloud-based end-to-end information environment that creates a valid simulation of any business enterprise economic reality. The BDT is built on the basis of the universal enterprise knowledge of Business Model Ontology, which enables its functional construct to overcome the limitation of software modularity and syncing necessities.
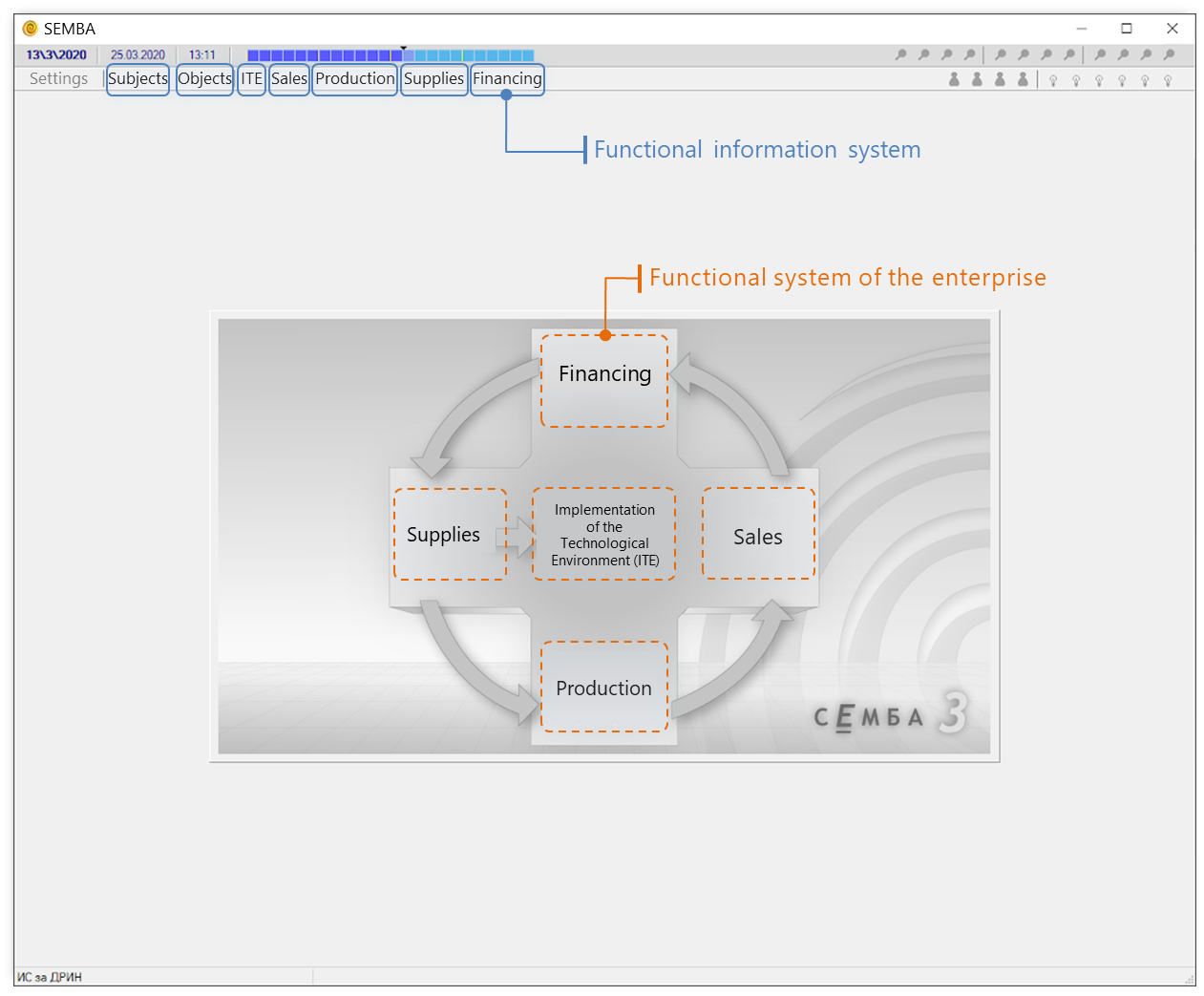
The BDT, being built on the BMO, ensures enterprise management efficiency by incorporating seven functional information spaces, covering the five technological systems of the enterprise together with its inherent objects and subjects. The seven functional information spaces (FIS) that drive efficiency and all-inclusive management of the business enterprise are: Subjects, Objects, Implementation of the Technological Environment, Sales, Internal Provision of Sales (Production), Supplies, Financing.
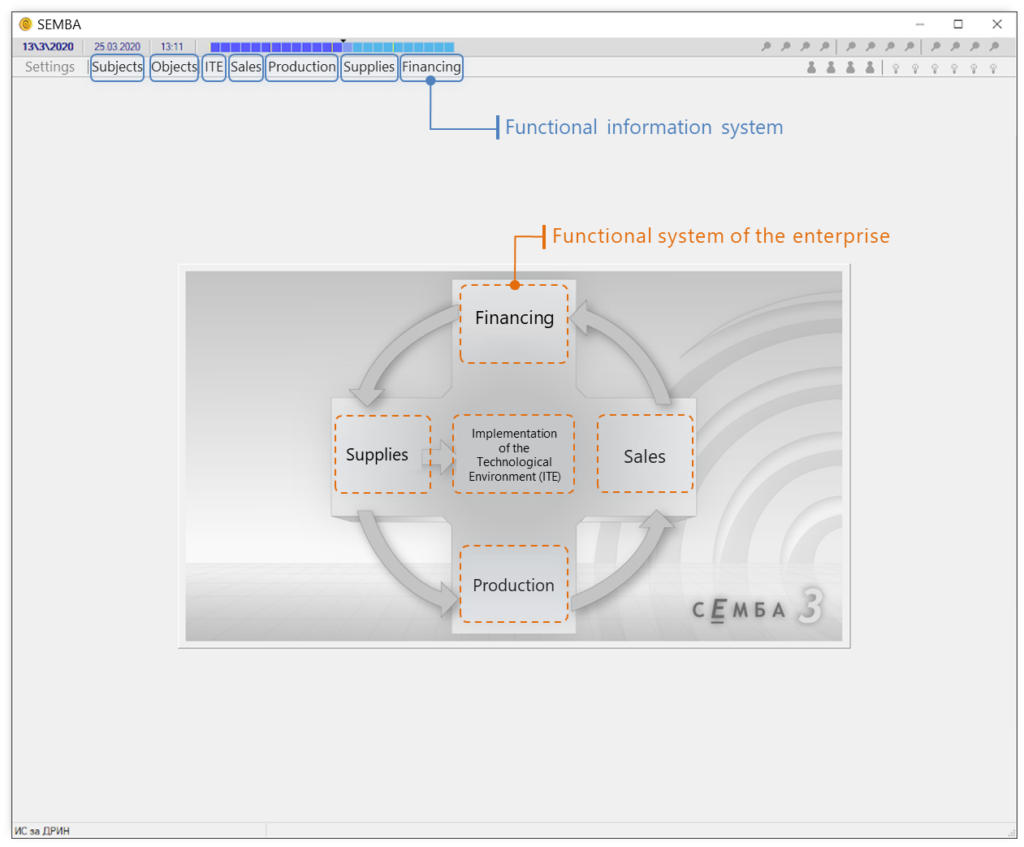
The BDT software is based on main principles including Initial integration, Intersystemicity, Unified approach, Operation in real-time, Modeling in variants and time intervals, Single and set management, and Feedback.
Initial integration
Initial integration
Initial integration of the functional systems, which form the construct of the BDT software, means that they should be interconnected by the logic of Business Model Ontology and thus cover the entire economy of the enterprise, so that there would be no need for expensive and endless processes of implementing a variety of informational environments (numerous modules, serving different fragments of the current knowledge of economy, and their databases). The initial integration is a consequence of the end-to-end scope, from which follow the properties of intersystemicity and unified approach.
Intersystemicity
Intersystemicity
Intersystemicity means that the process units and related data must be shared for the whole system. That is, provided that they have already been created in one functional system to be available for use by all other functional systems. For example, once an object has been designed after an order for principle engineering development, to be able to launch orders for Production or Sale for the exact same object and not for “some other” objects. Intersystemicity is a fundamental characteristic of the BDT software, which applies to all other characteristics and functionalities of the system.
Unified approach
Unified approach
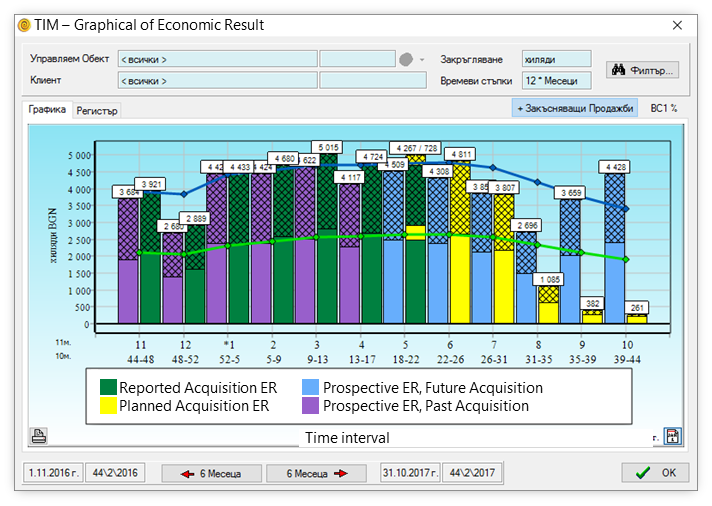
The unified approach includes the use of uniform classifiers, graphical and tabular time interval models (TIMs), registers, etc. The unified approach determines the achievement of high work efficiency and mobility of human resources. It reduces the time for training and implementation of the digital system and, at the same time, increases the level of overall understanding of employees about the principle of operation of each enterprise.
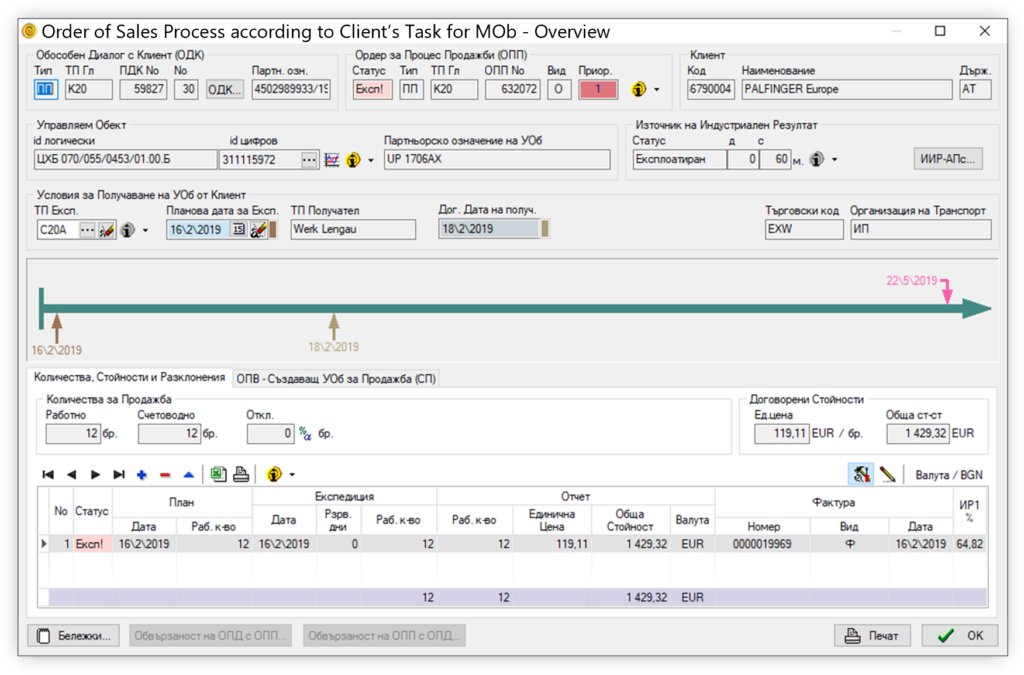
Operation in real-time
Operation in real-time
Operation in real-time means that all changes made to a process unit are reflected immediately in all affected Registers and time interval models (TIMs). For example, the creation of a Sales Order for an object instantly causes a change in the prospective stocks of the object in the respective warehouse. Or the reporting of the same Order as completed instantly changes (from planned to reported) the picture of the economic result of the enterprise, as well as the picture of the stock availability of the object in the respective warehouse.
Modeling in variants and time intervals
Modeling in variants and time intervals
All essential managerial parameters are modeled in time intervals in the BDT software. Simultaneously, for the same time interval, different variants of MOTELs (technological routes) are possible for the creation of the structure of a given product. This allows for multifaceted expansion of the system’s capabilities in strategic, tactical, and operational dimension. In this way, the system becomes an effective means of reengineering.
Feedback
Feedback
The state of an object in which the value of the deviation of a given parameter of the object exceeds the corresponding allowable limit is called Inadmissible Deviation. The occurrence of Inadmissible deviations is inevitable for any enterprise. A feedback entry point for identifying inadmissible deviations is every process in the 5 functional systems that make up the enterprise. Inadmissible deviations are subject to single and set management in order to be overcome on an ongoing basis (through specific measures) and to prevent their future occurrence (through the implementation of projects).
Single and set management
Single and set management
Single management concerns the analysis and change of parameters of a specific process unit. For example, dialogue with a customer, sales order, financial movement, etc. Set management concerns the screening of target sets of process units, their analysis, and taking action depending on the results. For example, in the register of customer dialogues, screening of all dialogues conducted with a specific customer for the current month. Or in the register of sales orders, screening the orders related to a specific customer group.
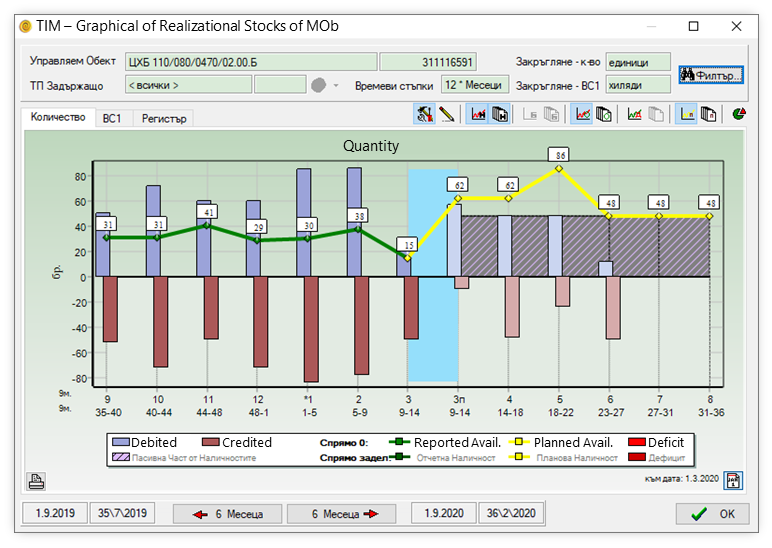
The creation of Business Digital Twin software is based on the scientific foundation of Business Model Ontology